RAID 5 Explained
RAID 5 (redundant array of independent disks) writes data across all disks in the volume and use a parity block for each data block.
Advantage
- RAID 5 offers comparable performance to RAID 0 with the benefit of protecting data.
- Read data transactions are very fast while write data transactions are somewhat slower (due to the parity that has to be calculated).
- RAID 5 is a configuration that uses disk striping with parity. Because data and parity are striped across all of the disks, no single disk is a bottleneck. Stripping.
Disadvantages
- If fails one-second disk before data can be rebuilt to the replacement hard drive, all information in the array will be lost.
- A minimum of three disks is required to create a RAID 5 volume.
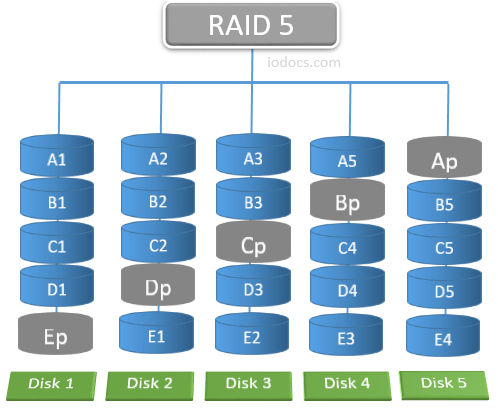
Array Capacity: (Size of Smallest Drive) * (Number of Drives – 1).

